

What is a Bi-Directional device & why are we talking about it?
This protective device is used in electrical installations to provide protection against faults where current flow is in both directions. Traditionally, protective devices such as circuit breakers are designed to only interrupt current flow on the load side.
Bi-Directional protective devices are important in systems where power can flow in both directions, such as those incorporating renewable energy sources, where power is given back to the grid.
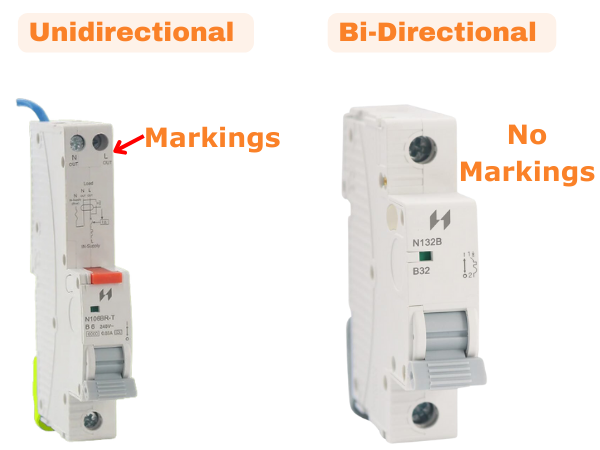

Difference In Devices
Unidirectional protective devices should be marked to specify the line and load terminals and are designed to operate when the power can only flow in one direction for example from the supply >>> load.
A Bi-Directional device does not have markings to specify line and load terminals where power can flow in either direction and will not cause damage. Always check with the manufacturer if you are unsure.
Why have we brought them into the newsletter this month? In the last few weeks The IET has proposed Amendment 3:2024 to BS7671:2018. You might be thinking "oh no loads of changes and a new book". Well this is not the case, as there is just one change, which you will be able to download and use to alongside the big brown book.

So essentially when a current can flow in both directions a Bi-Direction protective device must be used.
If you want to give feedback on this amendment you can click here, but you only have until the 5th of June 2024. Usually we are given 12 weeks to provide feedback but in this case we only had 4 weeks, this would indicate that the IET really wants to get this implemented quickly.
Below are some videos that detail the change from different perspectives.
IET Explanation
Video here!Manufacturers Perspective
Video here!

Last month we mentioned that we are doing a giveaway as a thank you to you our readers. We are giving one of you the opportunity to win all of the above tools and more.
All you have to do to be in with a chance of winning:
- Subscribe... which you are, otherwise you wouldn't see this
- Open and read 1 of the following volumes -June, July or August volumes
The winner of the giveaway will be randomly selected and announced within a special edition newsletter in August.


Consumer Units ✔️
Circuit Protection Devices ✔️
A brand that wont let you down...?
Verso, a trusted name in the consumer unit and circuit protection device industry, has recently undergone a rebranding and is now known as Navitas. This new identity reflects their commitment to innovation and energy, aligning perfectly with their mission to deliver top-tier electrical solutions.

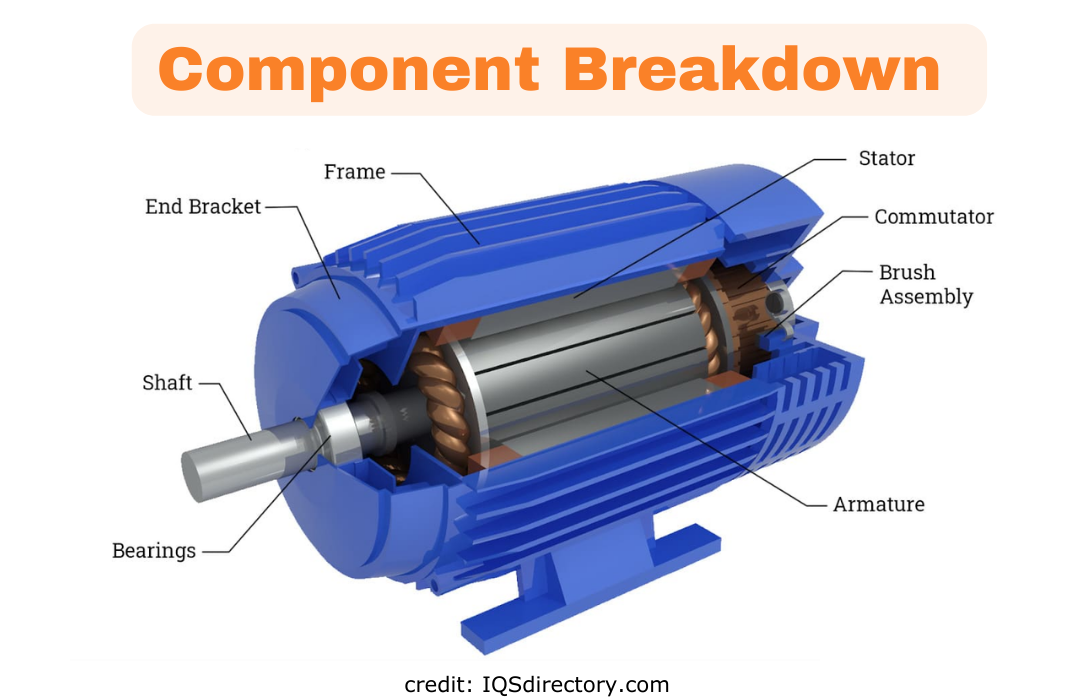
What Is A Motor?
A motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It works by electromagnetic induction, where an electric current creates a magnetic field that interacts with other magnetic fields to produce motion.
To keep it simple, when you give it electricity, it starts rotating, making it useful for many things like powering fans, pumps, machines and even vehicles.
Motor Configurations
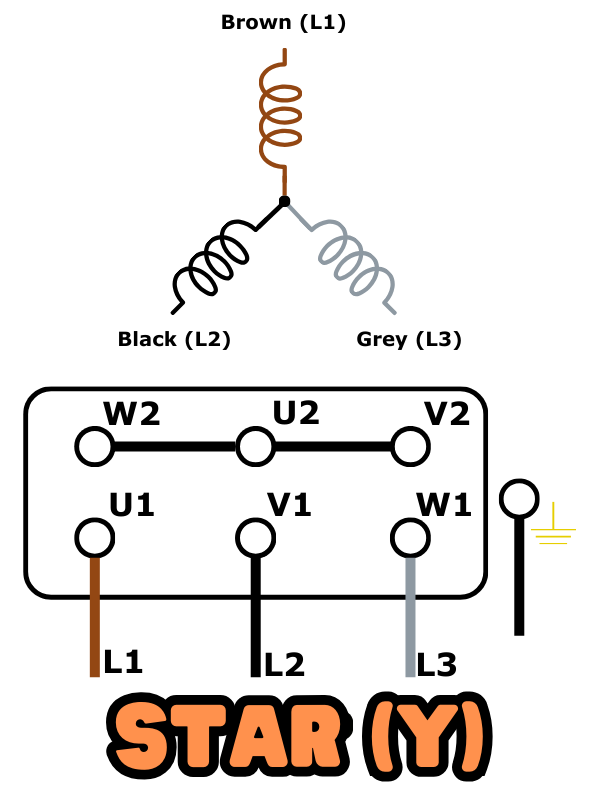
Star and delta are two different configurations used in three-phase induction motors.
Star (Y) Connection
- In a star connection, the three ends of the windings are connected to form a common point.
- Each winding is connected to a different phase of the three- phase power supply.
- Star-connected motors are typically used when the motor needs to start with a lower current draw.
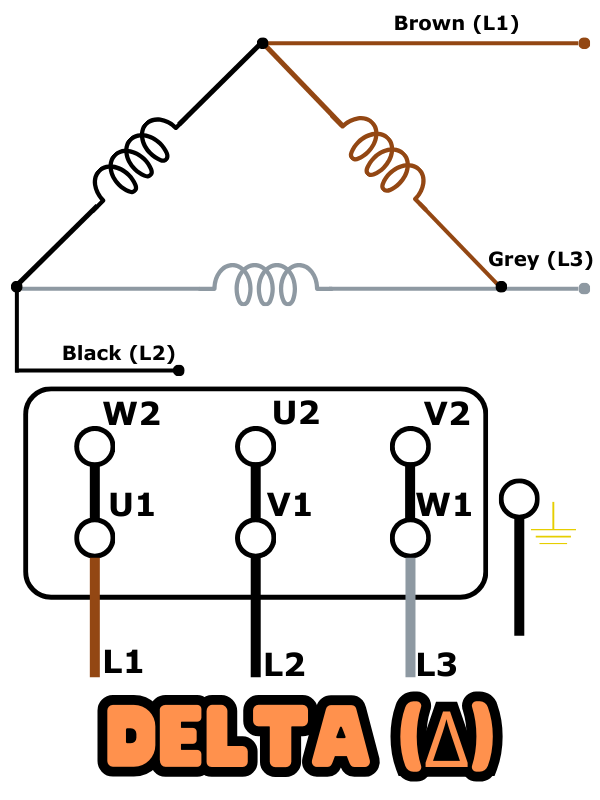
Delta (Δ) Connection
- In a delta connection, each winding is connected in series to form a closed loop, resembling the Greek letter delta (Δ).
- The three-phase power supply is directly connected to the ends of these windings.
- Delta-connected motors usually have higher starting torque compared to star-connected motors.
This shows the importance of the device, especially where they may be a high volume of people.

Below are 10 everyday items which you would find in your house. Your objective is to guess if the next answer is higher or lower than the last when it comes to its current draw (these are based on averages).
Start with a Hoover at an average of 6.25A
- Oven 🔺 or 🔽 Hoover?
- Toaster 🔺 or 🔽 Oven?
- Acti-fry 🔺 or 🔽 Toaster?
- TV 🔺 or 🔽 Acti-fry?
- Fridge 🔺 or 🔽 TV?
- Kettle 🔺 or 🔽 Fridge?
- Washing Machine 🔺 or 🔽 Kettle?
- Microwave 🔺 or 🔽 Washing Machine?
- Laptop 🔺 or 🔽 Microwave?

- Hoover = 6.25A
- 🔺 Oven = 14.6A
- 🔽 Toaster = 9A
- 🔽 Acti-fry = 6A
- 🔽 TV = 0.5A
- 🔺 Fridge = 4.5A
- 🔺 Kettle = 8A
- 🔺 Washing Machine = 10A
- 🔽 Microwave = 3A
- 🔽 Laptop 0.5A

If you are interested in becoming a sponsor of the newsletter or want to be featured like Mark above please don't hesitate to reach out. Link to contact us below
Contact us here!The material and information contained in this newsletter is for informational purpose only, you should not rely upon the material or information on this newsletter, all readers must make their own judgment and seek professional advice when making decisions based on the context of the newsletter